Software

GENFIT (and SASMOL)
GENFIT is a software tool for analysing small-angle scattering (SAS) data from X-ray (SAXS) or neutron (SANS) experiments. It reads in a set of one-dimensional scattering curves and fits them using different kinds of models. SAS curves calculated from a model can be smeared to allow for the instrumental resolution. The user can fit the experimental data selecting one or more models from a list including more than 30 models, starting from simple asymptotic behaviours (Guinier's law, Porod's law, etc.) down to complete atomic structures. Some models, which are defined in terms of both form and structure factors, take into account the interactions between particles in solution. GENFIT is able to simultaneously fit more SAS curves via a unique model or a mixture of models. In the latter case, some specific model parameters can be shared by any selection of the experimental curves. Model parameters can be related to the experimental chemical-physical conditions (temperature, pressure, concentration, pH, etc.) by means of link functions, which can be freely defined by the user. On the other hand, GENFIT can be used to generate theoretical SAS curves from a given model and/or from the knowledge of the species in solution. It can hence be a useful instrument to find the optimum experimental conditions for a planned SAS experiment. GENFIT is written in Fortran. Versions 2.0 and higher make use of a graphical user interface (GUI) to manage input files and execute the calculations.
GNXAS
The GNXAS package is a computer code for EXAFS data analysis based on multiple-scattering (MS) calculations and a rigorous fitting procedure of the raw experimental data. The main characteristic of the software are: + atomic phase shifts calculations in the muffin-tin approximation based on atom self-consistent relativistic calculations. Account for the neighbors is taken. + Inclusion of inelastic losses through complex Hedin-Lundqvist potential. + Calculation of MS signals associated with two, three, and four atom configurations using advanced algorithms. Use of an advanced fitting procedure that allows: + to fit simultaneously any number of spectra containing any number of edges, + to use directly the raw data without any pre-analysis, + to account for complex background multi-electron excitation features, + to use various model peaks for the pair, triplet and quadruplet distribution functions, including non Gaussian models and extreme cases. In all cases absolute parameters can be fitted, - to treat liquid phase or disordered systems and extract reliable g(r) functions in the short range, - to perform a rigorous statistical error analysis and plot two-dimensional correlation maps, - to provide a flexible scientific tool for EXAFS data analysis where the user has access to every stage of the calculation. - full modularity that makes easy to interface parts of the GNXAS software with other available software.
Grasp
"GRASansP" is a MatlabTM script application designed for the graphical inspection, analysis and reduction of multi-detector data produced by the Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS) instruments of the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL). GRASansP deals with many of the diverse requirements for analysis and reduction of SANS data using a general set of tools and reduction algorithms. Data from the two ILL SANS instruments, D11 and D22, as well as SANS instruments at some other neutron sources, are currently catered for in the GRASansP package. In principle the architecture and coding of GRASansP combined with the matrix handling abilities, graphics and other advantages of the Matlab™ environment should allow continued development of this software and be able to provide more general aspects of multi-detector and complex data set handling. The drive for producing such a suite of software came from the overwhelming need for a modern, complete and general-purpose package to deal with typical procedures required for analysis of two-dimensional SANS multidetector data. By it’s very nature, two-dimensional data is often best appreciated in a graphical form. The birth of GRASansP came from the need for graphical inspection and ability to be able to quickly process and extract the scattered intensity, I(q), as a function of position on the multidetector (qx,qy) or as a function of sample environment conditions from a series of many measurement runs (e.g. temperature sweep, rocking curve etc.). This, combined with an interest in scientific software development and the abilities of the Matlab™ environment have brought GRASansP into it’s present state.
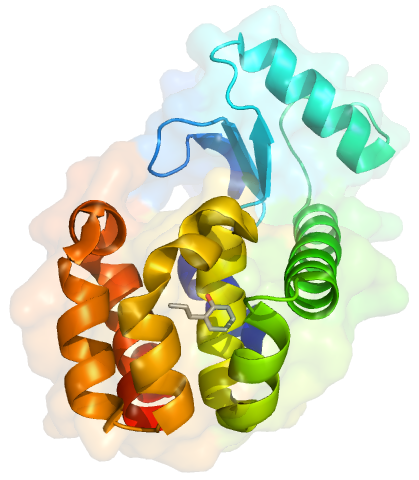
GROMACS
GROMACS (GROningen MAchine for Chemical Simulations) is a molecular dynamics and energy minimization package mainly designed to simulate the Newtonian equations of motion for systems with hundreds to millions of particles, typically of proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. GROMACS can run on CPUs and GPUs.
h5glance
H5Glance lets you conveniently explore HDF5 files in the terminal or an HTML interface, including in Jupyter notebooks.

h5nuvola - HDF5 services on the cloud
A web-based equivalent for HDFView which adds additional functionality. It implements Cloud file browsing, data visualisation services, and selective exporting of data. Its modular architecture includes an API facilitating data and metadata exploration through REST services. Back-end tasks are based on the Python framework Flask. HDF5 files are accessed through h5py. Bokeh plotting library handles the visualisation. The front-end uses HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript. h5nuvola is integrated in Elettra’s Virtual Unified Office. It can also be integrated with Jupyter.
H5Web
H5Web is a web-based HDF5 file viewer with NeXus support. It allows for the browsing and inspecting of the hierarchical structure of HDF5 files, as well as visualising their datasets as basic plots (1D, 2D). With H5Web, our intent is to provide synchrotron users with an easy-to-use application and to make open-source components available for other similar web applications. H5Web is built with React, a front-end web development library. It supports the exploration of HDF5 files, requested from a separate back-end for modularity (e.g. HSDS, Jupyter, etc.), and the visualisation of datasets using performant WebGL-based visualisations.

ICSD
Inorganic Crystal Structure Database, containing about 185,000 peer-reviewed data entries of inorganic and related structures, including their atomic coordinates dating back to 1913. It is produced cooperatively by FIZ Karlsruhe and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
idltomo
a graphical user interface to manage tomography data preprocessing, reconstruction and visualizaton based upon IDL and PyHST packages.
iFit
The iFit library (pronounce [eye-fit]) is a set of methods to load, analyse, plot, fit and optimize models, and export results. iFit is based on Matlab, but can also be launched without Matlab license (stand-alone version).Matlab It does not currently include advanced graphical user interfaces (GUI), and rather focuses on doing the math right. Any text file can be imported straight away, and a set of binary files are supported. Any data dimensionality can be handled, including event based data sets (even though not all methods do work for these). Any model can be assembled for fitting data sets. Last, a number of routines are dedicated to the analyses of S(q,w) and S(alpha,beta). More advanced features include the full automation to compute phonon dispersions in materials, using DFT codes such as ABINIT, ELK, VASP, QuantumEspresso, GPAW and more (Models/sqw_phonons). The software can also compute the neutron TAS resolution function (4D) and fits to experimental data with full resolution convolution (ResLibCal). An interface for McStas and McXtrace is also available to automate and optimize instrument simulations.
jupyterlab-h5web
JupyterLab extension to explore and visualize HDF5 file contents, using the web-based viewer H5Web. H5Web supports the NeXus format.
LAMP
LAMP (Large Array Manipulation Program) is designed for the treatment of data obtained from neutron scattering experiments at the Institut Laue-Langevin. However, LAMP is now a more general purpose application which can be seen as a GUI-laboratory for data analysis based on the IDL language.
MagDraw
Magnetic Editor Cell Constructor

MANTID
The Mantid project provides a framework that supports high-performance computing and visualisation of materials science data. Mantid has been created to manipulate and analyse neutron scattering and muon spectroscopy data, but could be applied to many other techniques.

Materials Studio
Materials Studio is a modeling and simulation environment designed to allow to predict and understand the relationships of a material’s atomic and molecular structure with its properties and behavior. With it one can construct, manipulate and view models of molecules, crystalline materials, surfaces, polymers, and mesoscale structures. Materials Studio includes quantum, atomistic (or “classical”), mesoscale, and statistical methods that enable one to evaluate materials at various particle sizes and time scales. It also includes tools for evaluating crystal structure and crystal growth.

