Software
PyFAI
pyFAI is an azimuthal integration library that tries to be fast (as fast as C and even more using OpenCL and GPU). It is based on histogramming of the 2theta/Q positions of each (center of) pixel weighted by the intensity of each pixel, but parallel version uses a SparseMatrix-DenseVector multiplication
PyHST2
Hybrid distributed code for high speed tomographic reconstruction with iterative reconstruction and a priori knowledge capabilities. PyHST2 (formerly known as PyHST) has been engineered to sustain the high data flow typical of the third generation synchrotron facilities (10 terabytes per experiment) by adopting a distributed and pipelined architecture. The code implements, beside a default filtered backprojection reconstruction, iterative reconstruction techniques with a-priori knowledge. The latter are used to improve the reconstruction quality or in order to reduce the required data volume and reach a given quality goal. The implemented a-priori knowledge techniques are based on the total variation penalisation and a new recently found convex functional which is based on overlapping patches.
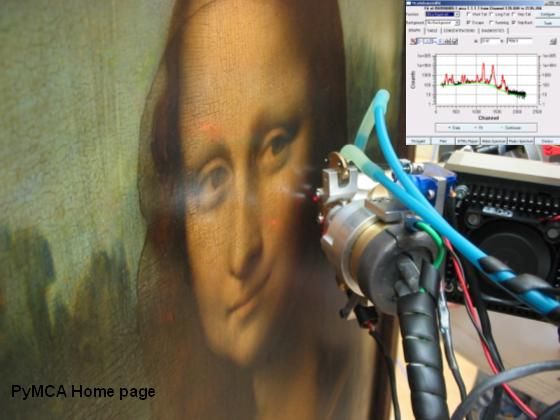
PyMca
X-ray Fluorescence Toolkit (visualization and analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence data). . The program allows both interactive and batch processing of large data sets and is particularly well suited for X-ray imaging. Its implementation of a complete description of the M shell is particularly helpful for analysis of data collected at low energies. It features, among many other things, the fundamental parameters method
PyNX
Python toolkit for accelerated Nano-structures Crystallography and Coherent X-ray Imaging techniques. The software included in this package can be used for: 1. the computing of X-ray scattering using graphical processing units 2. X-ray wavefield propagation (from near to far field) 3. simulation and GPU-accelerated analysis of experiments using the ptychography and coherent diffraction imaging techniques See the full documentation at: http://ftp.esrf.fr/pub/scisoft/PyNX/doc/
QENS library
This library provides different building blocks that users can combine, convolute and plug in different frameworks for visualizing or fitting Quasi Elastic Neutron Scattering (QENS) data S(Q, omega). It was developed as part of SINE2020 Workpackage 10 on Data Treatment to develop an exhaustive library of dynamical models in order to increase interoperability and modularity for a rapid prototyping. The models are written in Python for easy integration in workflows. In order to help users, a few examples of data analyses using different standard fitting engines (lmfit, scipy, bumps) are provided as Jupyter notebooks5. Tools are also provided to help those interested in contributing to the project by adding models or sharing examples of data treatment. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 654000.

Quantum Espresso
Quantum ESPRESSO (QE) is an integrated suite of Open-Source computer codes for ab initio quantum chemistry methods of electronic-structure calculations and materials modeling at the nanoscale. It is based on density functional theory, density functional perturbation theory, plane wave basisi sets, and pseudopotentials. The core plane wave DFT functions of QE are provided by the PWscf (Plane-Wave Self-Consistent Field) component,
Quanty
Quanty is a script language which allows the user to program quantum mechanical problems in second quantization and when possible solve these. It can be used in quantum chemistry as post Hartree-Fock or in one of the LDA++ schemes. (self consistent field, configuration interaction, coupled cluster, restricted active space, ...) The idea of Quanty is that the user can focus on the model and its physical or chemical meaning. Quanty takes care of the mathematics.
REFTIM
The program REFTIM calculates and fits the time spectra of nuclear resonant reflectivity, delayed and prompt reflectivity curves and the corresponding conversion electron Mössbauer spectra (CEMS) for any multilayer structure containing 57Fe, 151Eu, 149Sm, 119Sn or other isotopes if they have M1 Mössbauer transition. The experimental details of the nuclear resonance scattering technique with synchrotron radiation are described in the ID18 beamline Web pages.
RFit2000
RFIT2000 fits X-ray and neutron reflectivity data. The search of global minima is done via successive descent from local minima. This method can be treated as a two stage loop repeated consequently. The first stage is the local minimization with the ?2 -like criterion and the second one is the descent from the most recent local minimum. Reflectivity curve is calculated with one of the methods: Kinematic, Parratt and Matrix. Matrix method works faster for films modeled with multiple repetion of one identcal structural units. Film structure is represented with the box model. Each box is characterized with the scattering density (Re and Im), thickness and roughness of the top interface.
ROD
ROD is a program that can be used to do a refinement of a surface structure using surface X-ray diffraction data. All main features one encounters on surfaces, like roughness, relaxations, reconstructions and multiple domains, are taken into account. The most essential part of ROD is the calculation of the structure factor of the surface. ROD is complemented by two utilities: ANA and AVE: ANA can be used to integrate scans and to convert these into structure factors, while AVE can sort and average data, determine agreement factors and produce a data file for the program ROD.
SASfit
SASfit has been written for analyzing and plotting small angle scattering data. It can calculate integral structural parameters like radius of gyration, scattering invariant, Porod constant. Furthermore it can fit size distributions together with several form factors including different structure factors. Additionally an algorithm has been implemented, which allows to simultaneously fit several scattering curves with a common set of (global) parameters. This last option is especially important in contrast variation experiments or measurements with polarised neutrons. The global fit helps to determine fit parameters unambiguously which by analyzing a single curve would be otherwise strongly correlated.
SasView
SasView is a Small Angle Scattering (SAS) analysis package for the analysis of 1D and 2D scattering data directly in inverse space. The focus was originally on neutron data (SANS) but has been used for X-ray’s as well and includes a tool for determining a slit resolution for the SAXSess instrument. SansView also includes PrView to invert SAS data to P(r), a resolution calculator, and a scattering length density calculator among others tools. A simple plugin mechanism is available for users to add custom models.

Savu
Savu is a Python package to assist with the processing and reconstruction of parallel-beam tomography data. The project originated in the Data Analysis Group at the Diamond Light Source (UK synchrotron) to address the growing, and increasingly complex, needs of the tomography community. Designed to allow greater flexibility in tomography data processing, Savu is capable of processing N-dimensional full-field tomography and mapping tomography data, along with concurrent processing of multiple datasets such as those collected as part of a multi-modal setup. Savu process lists, tailored to a specific experiment and passed to the framework at runtime along with the data, detail the processing steps that are required. A Savu process list is created using the Savu configurator tool, which stacks together plugins chosen from a repository. Each plugin performs a specific independent task, such as correction, filtering, reconstruction. For a list of available plugins see plugin API. Savu is currently in use across the tomography beamlines at Diamond to reconstruct both full-field tomography data and multi-modal, mapping tomography data.
SAXSutilities
Matlab based graphical user interfaces for the online processing and analysis of Small Angle X-ray Scattering data. In particular: -online treatment and fitting of SAXS data -averaging, background subtraction, normalization of ASCII data, etc. -processing of 2D SAXS images -averaging, subtraction, etc. of EDF images
SHARP/autoSHARP
SHARP is a computer program for macromolecular crystallography. It operates on reduced, merged and scaled data from SIR(AS), MIR(AS) and MAD experiments, refines the heavy-atom model, helps detect minor or disordered sites using likelihood-based residual maps, and calculates phase probability distributions for all reflections in the data set. autoSHARP is an automated structure solution system - from merged data to automatic model building (uses SHARP as phasing engine).

